Setting up a remote desktop allows you to access your computer wherever you are and control it as if you were directly in front of the keyboard. By using the built-in Remote Desktop Connection app in Windows 10, you can troubleshoot issues, access files, and so much more. Here’s how to set up a remote desktop in Windows 10 and how to remotely access another computer over the internet.
May 15, 2020 If the remote device is another computer running Windows 10, download Microsoft’s Remote Desktop app from the Microsoft Store to streamline the process of setting up remote access. By default, remote desktop saves the settings for a remote desktop session in a file called Default.rdp. In Windows 7, Default.rdp saves by default to the%homedrive%%homepathDocuments directory. You can edit this file by right-clicking it and selecting Edit. The Remote Desktop Connection dialog that appears has a Display tab.
How to Set Up Remote Desktop Windows 10

To set up a remote desktop in Windows 10, go to Settings > System > Remote Desktop. Then turn on the slider for Enable Remote Desktop. Next, search Settings for Allow an app through Windows firewall and enable the Remote Desktop app for Private and Public.
Note: You can only run the Remote Desktop Connection app if you are using Windows 10 Professional or Enterprise. If you are using Windows 10 Home edition, check out our guide on how to use Quick Assist to remotely control a computer.
- Click the Windows Start button. This is the button with the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of your screen. Do this from the host computer (or the computer you will be trying to access remotely).
- Then click Settings. This is the gear-shaped icon just above the power button.
- Next, click System.
- Then click Remote Desktop in the left sidebar. You can find this by scrolling down. It is the icon that looks like greater than and less than signs pointing at each other.
- Next, click the slider next to Enable Remote Desktop. This will cause a new window to pop up.
- Then click Confirm. A pop-up box appears asking you if you would like to enable remote desktop. It also reminds you that doing so will allow you and other users in your User accounts to connect to the PC remotely. Then you will need to change your firewall settings in order to access another computer over the internet.
- Next, type firewall into the search bar of the Settings window. You can do this by clicking the search box that says Find a setting at the top of the left sidebar. Once you type firewall, you will see search results populated under the search bar.
- Then choose Allow an app through Windows firewall. If you don’t see this option, click Show All, and then select it from the list.
- Then click Change settings. Initially, the apps and the checkboxes beside them will be grey or disabled. Once you click Change settings, they will turn black and become enabled.
- Tick the Private and Publiccheckboxes to the right of Remote Desktop. Make sure both that the boxes under the Private and Public columns are checked.
- Finally, click OK.
Once you enable your remote desktop and allow the app to communicate through your firewall, you can access that computer over the internet. Here’s how:
How to Remotely Access Another Computer Over the Internet
Microsoft Rewards
There are two ways you can remotely access another computer over the internet – depending on whether you’re on the same network or not. If you are accessing another computer within the same network, you just need to know the PC name. If otherwise, you need to know your public IP and set up port forwarding.
How to Remotely Access Another Computer Over the Internet Within Your Network
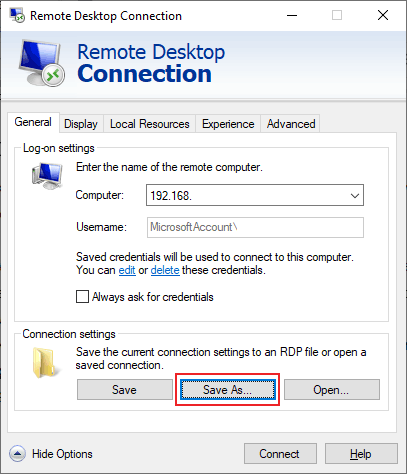
To remotely access another computer within your network over the internet, open the Remote Desktop Connection app and enter that computer’s name, and your username and password.
- Click the magnifying glass icon in the bottom-left corner of your screen. Do this from the computer you want to access over the internet.
- Then type About into the search bar and click Open.
- Next, copy your computer’s name. You can find this next to Device name. You can either write this name down, or copy and paste it into a text document, an email, or any other method that you want.
Note: If this name is too complicated, you can click the Rename this PC button below. This lets you choose your own name for your PC.
- Then open the Windows search bar and type remote desktop connection. This is the magnifying glass icon in the bottom-left corner of your screen.Do this from the client computer or the computer that you will use to establish the remote connection.
- Next, click Open.
- Then click Show Options. You can see this in the bottom-left corner of the window.
- Next, enter the computer’s name. This is the name that you copied down in the previous steps.
- Also, enter the username. If this information is filled in already, make sure it is correct. You can find your username by going to Settings > Accounts. Then you will see your username under your profile image.
- Then click Connect.
Note: You can also change additional settings by clicking the Display, Local Resources, Experience, and Advanced tabs.
- Next, enter your computer’s password and click OK. This is the password that you use to sign in to the computer when you are on the lock screen.
Note: You might encounter a prompt asking you if you want to connect even if the identity of the remote computer cannot be identified. Just click on Yes.
- Finally, wait for the remote connection to be configured. After the step above, you will see a green progress bar. Wait for it to complete. Briefly, you will see a black window which turns to blue. Once the remote connection is successfully established, you will see a view of the computer you’re trying to access.
How to Remotely Access Another Computer Outside Your Network
Microsoft Remote Desktop Assistant
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services
- Open a web browser. Do this from the host computer or the computer you will be trying to access remotely.
- Then type what is my IP into the address bar.
- Next, copy the public IP address listed. Your public IP address will be a series of numbers separated by periods.
Note: Do not share your public IP address with anyone you don’t trust. They can use this information to hack your computer and steal your personal information, such as bank details.
- Then open TCP port 3389 on your router. If you don’t know how to do this, check out our step-by-step guide on how to port forward.
Note: You should also set a static IP address for the computer you are trying to access. If you want to know how to set a static IP address for your Windows 10 PC, check out our step-by-step guide here.
- Next, open the Remote Desktop Connection app. Do this from the client computer (or the one you will use to remotely control the host computer).
- Enter your public IP address in the Computer field. This will be the public IP address you copied down earlier.
- Then click Connect.
- Enter your credentials. On the Windows Security page, type in the username and password of your remote server.
- Click OK.
Note: You might encounter a prompt asking you if you want to connect even if the identity of the remote computer cannot be identified. Just click on Yes.
- Finally, wait for the remote connection to be configured. After the step above, you will see a green progress bar. Wait for it to complete. Briefly, you will see a black window which turns to blue. Once the remote connection is successfully established, you will see a view of the computer you’re trying to access.
If you’re looking for a less complicated way of accessing your computer remotely, check out our article on how to remotely control a Windows 10 or Mac computer.
Was this article helpful?
Related Articles
The following table includes the list of supported RDP file settings that you can use with the Remote Desktop clients. When configuring settings, check Client comparisons to see which redirections each client supports.
The table also highlights which settings are supported as custom properties with Windows Virtual Desktop. You can refer to this documentation detailing how to use PowerShell to customize RDP properties for Windows Virtual Desktop host pools.
Connection information
| RDP setting | Description | Values | Default value | Windows Virtual Desktop support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| full address:s:value | PC Name: This setting specifies the name or IP address of the remote computer that you want to connect to. This is the only required setting in an RDP file. | A valid name, IPv4 address, or IPv6 address. | No | |
| alternate full address:s:value | Specifies an alternate name or IP address of the remote computer. | A valid name, IPv4 address, or IPv6 address. | No | |
| username:s:value | Specifies the name of the user account that will be used to sign in to the remote computer. | Any valid username. | No | |
| domain:s:value | Specifies the name of the domain in which the user account that will be used to sign in to the remote computer is located. | A valid domain name, such as 'CONTOSO'. | No | |
| gatewayhostname:s:value | Specifies the RD Gateway host name. | A valid name, IPv4 address, or IPv6 address. | No | |
| gatewaycredentialssource:i:value | Specifies the RD Gateway authentication method. | - 0: Ask for password (NTLM) - 1: Use smart card - 2: Use the credentials for the currently logged on user. - 3: Prompt the user for their credentials and use basic authentication - 4: Allow user to select later - 5: Use cookie-based authentication | 0 | No |
| gatewayprofileusagemethod:i:value | Specifies whether to use default RD Gateway settings. | - 0: Use the default profile mode, as specified by the administrator - 1: Use explicit settings, as specified by the user | 0 | No |
| gatewayusagemethod:i:value | Specifies when to use an RD Gateway for the connection. | - 0: Don't use an RD Gateway - 1: Always use an RD Gateway - 2: Use an RD Gateway if a direct connection cannot be made to the RD Session Host - 3: Use the default RD Gateway settings - 4: Don't use an RD Gateway, bypass gateway for local addresses Setting this property value to 0 or 4 are effectively equivalent, but setting this property to 4 enables the option to bypass local addresses. | 0 | No |
| promptcredentialonce:i:value | Determines whether a user's credentials are saved and used for both the RD Gateway and the remote computer. | - 0: Remote session will not use the same credentials - 1: Remote session will use the same credentials | 1 | No |
| authentication level:i:value | Defines the server authentication level settings. | - 0: If server authentication fails, connect to the computer without warning (Connect and don't warn me) - 1: If server authentication fails, don't establish a connection (Don't connect) - 2: If server authentication fails, show a warning and allow me to connect or refuse the connection (Warn me) - 3: No authentication requirement specified. | 3 | No |
| enablecredsspsupport:i:value | Determines whether the client will use the Credential Security Support Provider (CredSSP) for authentication if it is available. | - 0: RDP will not use CredSSP, even if the operating system supports CredSSP - 1: RDP will use CredSSP if the operating system supports CredSSP | 1 | Yes |
| disableconnectionsharing:i:value | Determines whether the client reconnects to any existing disconnected session or initiate a new connection when a new connection is launched. | - 0: Reconnect to any existing session - 1: Initiate new connection | 0 | No |
| alternate shell:s:value | Specifies a program to be started automatically in the remote session as the shell instead of explorer. | Valid path to an executable file, such as 'C:ProgramFilesOfficeword.exe' | Yes |
Windows Remote Desktop Settings
Session behavior
| RDP setting | Description | Values | Default value | Windows Virtual Desktop support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| autoreconnection enabled:i:value | Determines whether the client will automatically try to reconnect to the remote computer if the connection is dropped, such as when there's a network connectivity interruption. | - 0: Client does not automatically try to reconnect - 1: Client automatically tries to reconnect | 1 | Yes |
| bandwidthautodetect:i:value | Determines whether or not to use automatic network bandwidth detection. Requires bandwidthautodetect to be set to 1. | - 0: Disable automatic network type detection - 1: Enable automatic network type detection | 1 | Yes |
| networkautodetect:i:value | Determines whether automatic network type detection is enabled | - 0: Don't use automatic network bandwidth detection - 1: Use automatic network bandwidth detection | 1 | Yes |
| compression:i:value | Determines whether bulk compression is enabled when it is transmitted by RDP to the local computer. | - 0: Disable RDP bulk compression - 1: Enable RDP bulk compression | 1 | Yes |
| videoplaybackmode:i:value | Determines if the connection will use RDP-efficient multimedia streaming for video playback. | - 0: Don't use RDP efficient multimedia streaming for video playback - 1: Use RDP-efficient multimedia streaming for video playback when possible | 1 | Yes |
Device redirection
Microsoft Remote Desktop App Setup
| RDP setting | Description | Values | Default value | Windows Virtual Desktop support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| audiocapturemode:i:value | Microphone redirection: Indicates whether audio input redirection is enabled. | - 0: Disable audio capture from the local device - 1: Enable audio capture from the local device and redirection to an audio application in the remote session | 0 | Yes |
| encode redirected video capture:i:value | Enables or disables encoding of redirected video. | - 0: Disable encoding of redirected video - 1: Enable encoding of redirected video | 1 | Yes |
| redirected video capture encoding quality:i:value | Controls the quality of encoded video. | - 0: High compression video. Quality may suffer when there is a lot of motion. - 1: Medium compression. - 2: Low compression video with high picture quality. | 0 | Yes |
| audiomode:i:value | Audio output location: Determines whether the local or remote machine plays audio. | - 0: Play sounds on the local computer (Play on this computer) - 1: Play sounds on the remote computer (Play on remote computer) - 2: Do not play sounds (Do not play) | 0 | Yes |
| camerastoredirect:s:value | Camera redirection: Configures which cameras to redirect. This setting uses a semicolon-delimited list of KSCATEGORY_VIDEO_CAMERA interfaces of cameras enabled for redirection. | - * : Redirect all cameras - List of cameras, such as camerastoredirect:s:?usb#vid_0bda&pid_58b0&mi - One can exclude a specific camera by prepending the symbolic link string with '-' | Don't redirect any cameras | Yes |
| devicestoredirect:s:value | Plug and play device redirection: Determines which devices on the local computer will be redirected and available in the remote session. | - *: Redirect all supported devices, including ones that are connected later - Valid hardware ID for one or more devices - DynamicDevices: Redirect all supported devices that are connected later | Don't redirect any devices | Yes |
| drivestoredirect:s:value | Drive/storage redirection: Determines which disk drives on the local computer will be redirected and available in the remote session. | - No value specified: don't redirect any drives - * : Redirect all disk drives, including drives that are connected later - DynamicDrives: redirect any drives that are connected later - The drive and labels for one or more drives, such as 'drivestoredirect:s:C:;E:;': redirect the specified drive(s) | Don't redirect any drives | Yes |
| keyboardhook:i:value | Determines when Windows key combinations (WIN key, ALT+TAB) are applied to the remote session for desktop connections. | - 0: Windows key combinations are applied on the local computer - 1: Windows key combinations are applied on the remote computer when in focus - 2: Windows key combinations are applied on the remote computer in full screen mode only | 2 | Yes |
| redirectclipboard:i:value | Clipboard redirection: Determines whether clipboard redirection is enabled. | - 0: Clipboard on local computer isn't available in remote session - 1: Clipboard on local computer is available in remote session | 1 | Yes |
| redirectcomports:i:value | COM ports redirection: Determines whether COM (serial) ports on the local computer will be redirected and available in the remote session. | - 0: COM ports on the local computer are not available in the remote session - 1: COM ports on the local computer are available in the remote session | 0 | Yes |
| redirectprinters:i:value | Printer redirection: Determines whether printers configured on the local computer will be redirected and available in the remote session | - 0: The printers on the local computer are not available in the remote session - 1: The printers on the local computer are available in the remote session | 1 | Yes |
| redirectsmartcards:i:value | Smart card redirection: Determines whether smart card devices on the local computer will be redirected and available in the remote session. | - 0: The smart card device on the local computer is not available in the remote session - 1: The smart card device on the local computer is available in the remote session | 1 | Yes |
| usbdevicestoredirect:s:value | USB redirection | - *: Redirect all USB devices that are not already redirected by another high-level redirection - {Device Setup Class GUID}: Redirect all devices that are members of the specified device setup class - USBInstanceID: Redirect a specific USB device identified by the instance ID | Don't redirect any USB devices | Yes |
Display settings
| RDP setting | Description | Values | Default value | Windows Virtual Desktop support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| use multimon:i:value | Determines whether the remote session will use one or multiple displays from the local computer. | - 0: Don't enable multiple display support - 1: Enable multiple display support | 1 | Yes |
| selectedmonitors:s:value | Specifies which local displays to use from the remote session. The selected displays must be contiguous. Requires use multimon to be set to 1. Only available on the Windows Inbox (MSTSC) and Windows Desktop (MSRDC) clients. | Comma separated list of machine-specific display IDs. IDs can be retrieved by calling mstsc.exe /l. The first ID listed will be set as the primary display in the session. | All displays | Yes |
| maximizetocurrentdisplays:i:value | Determines which display the remote session goes full screen on when maximizing. Requires use multimon to be set to 1. Only available on the Windows Desktop (MSRDC) client. | - 0: Session goes full screen on the displays initially selected when maximizing - 1: Session dynamically goes full screen on the displays touched by the session window when maximizing | 0 | Yes |
| singlemoninwindowedmode:i:value | Determines whether a multi display remote session automatically switches to single display when exiting full screen. Requires use multimon to be set to 1. Only available on the Windows Desktop (MSRDC) client. | - 0: Session retains all displays when exiting full screen - 1: Session switches to single display when exiting full screen | 0 | Yes |
| screen mode id:i:value | Determines whether the remote session window appears full screen when you launch the connection. | - 1: The remote session will appear in a window - 2: The remote session will appear full screen | 2 | Yes |
| smart sizing:i:value | Determines whether or not the local computer scales the content of the remote session to fit the window size. | - 0: The local window content won't scale when resized - 1: The local window content will scale when resized | 0 | Yes |
| dynamic resolution:i:value | Determines whether the resolution of the remote session is automatically updated when the local window is resized. | - 0: Session resolution remains static for the duration of the session - 1: Session resolution updates as the local window resizes | 1 | Yes |
| desktop size id:i:value | Specifies the dimensions of the remote session desktop from a set of pre-defined options. This setting is overridden if desktopheight and desktopwidth are specified. | -0: 640×480 - 1: 800×600 - 2: 1024×768 - 3: 1280×1024 - 4: 1600×1200 | 1 | Yes |
| desktopheight:i:value | Specifies the resolution height (in pixels) of the remote session. | Numerical value between 200 and 8192 | Match the local computer | Yes |
| desktopwidth:i:value | Specifies the resolution width (in pixels) of the remote session. | Numerical value between 200 and 8192 | Match the local computer | Yes |
| desktopscalefactor:i:value | Specifies the scale factor of the remote session to make the content appear larger. | Numerical value from the following list: 100, 125, 150, 175, 200, 250, 300, 400, 500 | 100 | Yes |
RemoteApp
Microsoft Remote Desktop Settings Mac

Microsoft Remote Desktop Access
| RDP setting | Description | Values | Default value | Windows Virtual Desktop support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| remoteapplicationcmdline:s:value | Optional command-line parameters for the RemoteApp. | Valid command-line parameters. | No | |
| remoteapplicationexpandcmdline:i:value | Determines whether environment variables contained in the RemoteApp command-line parameter should be expanded locally or remotely. | - 0: Environment variables should be expanded to the values of the local computer - 1: Environment variables should be expanded to the values of the remote computer | 1 | No |
| remoteapplicationexpandworkingdir:i:value | Determines whether environment variables contained in the RemoteApp working directory parameter should be expanded locally or remotely. | - 0: Environment variables should be expanded to the values of the local computer - 1: Environment variables should be expanded to the values of the remote computer. The RemoteApp working directory is specified through the shell working directory parameter. | 1 | No |
| remoteapplicationfile:s:value | Specifies a file to be opened on the remote computer by the RemoteApp. For local files to be opened, you must also enable drive redirection for the source drive. | Valid file path. | No | |
| remoteapplicationicon:s:value | Specifies the icon file to be displayed in the client UI while launching a RemoteApp. If no file name is specified, the client will use the standard Remote Desktop icon. Only '.ico' files are supported. | Valid file path. | No | |
| remoteapplicationmode:i:value | Determines whether a connection is launched as a RemoteApp session. | - 0: Don't launch a RemoteApp session - 1: Launch a RemoteApp session | 1 | No |
| remoteapplicationname:s:value | Specifies the name of the RemoteApp in the client interface while starting the RemoteApp. | App display name. For example, 'Excel 2016.' | No | |
| remoteapplicationprogram:s:value | Specifies the alias or executable name of the RemoteApp. | Valid alias or name. For example, 'EXCEL.' | No |